As the world races toward an even more digitally connected future, 5G (or fifth generation) technology is increasingly in the spotlight. The promise: more throughput, less lag, and massive connectivity potential. But amidst all the fanfare, a crucial question still remains. Is 5G truly necessary?
We all know you can’t stop progress. But progress must come with practical applications. So let’s take a deep look at the architecture of 5G, what 5G providers can do (and are doing), what a 5G platform entails, and what it all means for service providers today. And all in a (mostly) Q&A format! Our aim is to peel back the layers of the 5G debate, examining specific cases where its impact is both transformational and necessary. Along the way, we’ll look at the basics of 5G, from the innovations that are wrapped in with it to the real-world challenges and opportunities it presents. And, in the name of balance, we’ll address a few scenarios where the technology may not yet be a practical investment for telecoms.
The Test Lab: 5G in Africa
Before we dive into the questions, let’s begin at the beginning. (Or, at least, at the birthplace of us all.) 5G is gaining fast ground in Africa. Uganda launched its first 5G network in 2023. In Kenya, in particular, 5G adoption has seen a remarkable uptake. Over half a million users are currently tapping into 5G wireless technology there. (In fact, uptake in Kenya spiked over 13% in the three months between June and September 2023 – a trend that one provider, Safaricom, said would enable more options for retail and enterprise clients in the country.) According to a report by the GSMA, there will be an estimated 340 million 5G connections across Africa by 2030.
Why does 5G seem so accelerated in Africa? In short, high mobile uptake. “With more than 1.2 billion connections and over 650 million unique mobile users… mobile has a greater reach in Africa than any other technology, making it an important enabler of social and economic progress in the region,” writes the GSMA. “In this sense, 5G is a necessary upgrade to the mobile product, ensuring that it continues to remain relevant to consumers, enterprises, governments, and society as a whole.”
Future Potential vs. Present Reality
But the road to 5G buildout in Africa is long, and not straight. Nor is it equal, yet. South Africa was one of the first countries on the continent to launch its 5G network (in 2020, when Vodacom and MTN launched a 5G mobile and fixed wireless service). But in many regions, like Nigeria, new mobile network operators are still strategizing the integration of 4G and 5G amidst ongoing issues with legacy networks.
Economics, of course, plays a role. “The greatest potential obstacle to consumer 5G adoption and usage in Africa is device cost and availability,” says the GSMA in its report. To get over that barrier for the retail market, providers will need to offer extensive device financing options. Meanwhile, the GSMA also points to the need for changes to the overall policy environment, more funding for small-cell deployment, and more development of renewable energy to power those remote cells.
Okay, super interesting, yes. But why do we lead with these specific-to-Africa issues before we dig into our larger Q&A about the present and future of 5G? Because, fittingly, just as Africa was the cradle of humanity, the driving economic shifts of widening 5G development are turning the continent into the cradle of telecom innovation. So, if you are interested in how 5G is going to transform cities and economies, then you’ll want to keep an eye on countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa.
Meanwhile, let’s kick off our 5G Q&A.
The Architecture of 5G: A Q&A
To begin, let’s get into the nuts and bolts. In our first set of questions, we’re going to take a quick higher-level look at 5G architecture from a layperson’s perspective. If you want to open the proverbial car bonnet and get your hands dirty in the technical works, you can find very detailed breakdowns on how 5G wireless differs from previous generations here and here.

What is the architecture of 5G, and how is it structured?
5G architecture is fundamentally designed to be highly flexible and scalable, supporting a wide array of applications and services. It introduces a layered approach that separates the user plane (the data traffic) from the control plane (the signaling traffic). This allows for more efficient network management and optimization.
The core components of 5G include the Next Generation Core (NGC), which supports end-to-end network slicing, and advanced Radio Access Networks (RAN) that utilize technologies like massive MIMO and beamforming to enhance connectivity and bandwidth management. (If you’re saying “What?” at those terms, read on to the next bit.)
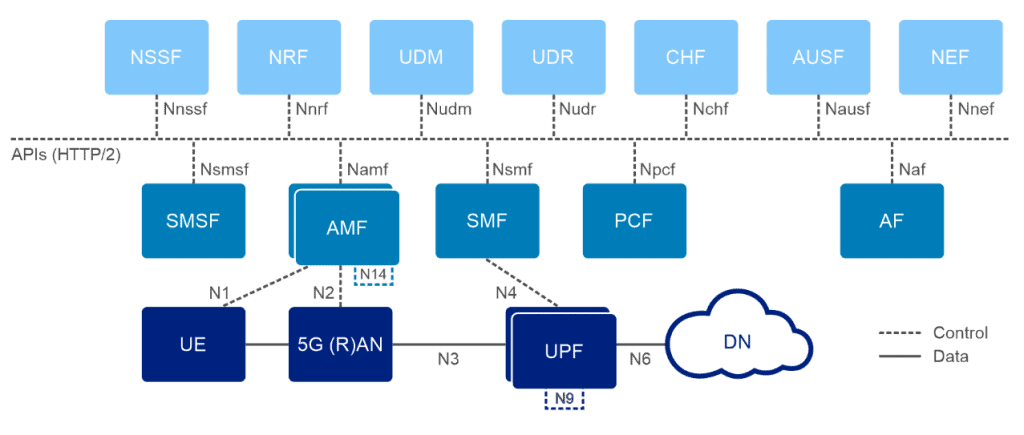
What technological innovations are incorporated into 5G architecture?
Some of those fancy terms you just read are the key innovations in 5G architecture. Here’s what they mean:
- Massive MIMO: This is a system that uses hundreds of antennas at a single cell (on both the receiver and transmitter sides) to significantly increase capacity and coverage.
- Beamforming: This technology focuses a wireless signal toward a specific receiving device rather than having the signal spread in broad directions. Beamforming improves both speed and efficiency.
- Edge Computing: This is a form of distributed IT architecture. Rather than sending data across long distances to be processed at some far-away data center, edge computing moves that processing closer to the user. (In other words, to the “edge” of the network.) This reduces traffic and latency (i.e., it makes things faster) through central networks.
- Network Slicing: This enables the creation of multiple virtual networks that operate on the same physical hardware. The benefit of network slicing is that you can tailor each network to suit the specific needs of different customers.
How does 5G architecture impact network performance and reliability?
It’s generally accepted that 5G architecture can dramatically improve network performance and reliability. By incorporating those advanced technologies we defined in the answer above, the fifth generation of cellular networks shows higher speed, lower latency, and more overall reliability. This is especially true for critical communications services that require extreme speed and high levels of data integrity.
What new advancements does 5G bring to wireless communication?
Beyond that improved performance, 5G represents several key advancements. With the adoption of higher frequency bands, particularly millimeter waves, 5G networks achieve faster data transmission rates. 5G also introduces Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC), which is crucial for applications that require instantaneous response times.
What are the advantages compared to previous network generations?
Compared to 4G, 5G offers significantly faster speeds, a greater capacity for data traffic, and, as we’ve explained, much lower latency. These improvements are due to the use of a wider range of frequency bands, those advanced antenna technologies we talked about, and more efficient network architectures. 5G is designed to support up to 1 million devices per square kilometer. That represents a tenfold increase over 4G. (Yes, 10X!) What’s particularly important here is that this is what will support the ongoing and massive expansion of IoT devices.
A Look at the Protocol for 5G
Now let’s drill down a bit into the backbone of 5G: the standards that support the interaction between 5G infrastructure, the 5G providers, and the devices that ordinary people and businesses (or machines, for that matter) are actually using. Basically, how the data moves.
How exactly do 5G protocols enhance speed and reliability?
These protocols optimize packet scheduling and feature robust error correction mechanisms. Packet scheduling in 5G dynamically allocates bandwidth based on user demand and network conditions, which maximizes throughput and reduces delays. The error correction mechanisms ensure data integrity and facilitate quick recovery from transmission errors, thus enhancing the overall reliability of the network.
How do the protocols differ from those of previous network generations?
Compared to previous generations, 5G protocols are designed to be more flexible and scalable, supporting a wider range of services and applications. They are also more efficient in handling large volumes of data and high-speed connections, thanks to those advances in technology we talked about earlier, a.k.a. MIMO and beamforming.
5G protocols significantly impact the development of new technologies and services by:
- Facilitating lower latency: Yes, we are throwing the word latency around a lot, but that’s because it’s important. Low latency is essential for the development of real-time applications such as VR and autonomous systems.
- Supporting higher throughput: In other words, it enables services that require high data rates, such as 4K video streaming and large-scale cloud applications.
What challenges and issues are associated with developing and implementing 5G protocols?
While the cost of infrastructure and security often dominate discussions about 5G technology, the protocols used in its deployment present their own set of challenges. These include ensuring interoperability with existing technologies and managing the increased complexity of network operations. Additionally, adherence to diverse regulatory standards across different regions adds a layer of complexity to the deployment of 5G protocols.
What About the Platform?
So, we have the infrastructure, and we have the protocols. But how are they put into use? That’s where the 5G platform comes in. But the word here is a bit deceiving, because a 5G platform is not just one discrete thing. In short, a 5G platform is a comprehensive suite of technologies and architectural components designed to deliver advanced network services. Here are a few FAQs that can help break those platform pieces down.

What are the key components of the 5G platform?
A 5G platform includes several interconnected components that together enhance the capabilities of mobile communication. The platform’s backbone is that 5G New Radio (NR) interface we mentioned above. It’s a new wireless air interface standard that surpasses LTE technology by offering higher data rates, reduced latency, and greater flexibility. It utilizes diverse spectrum bands such as sub-6 GHz for broad coverage and mmWave for high-capacity, short-range communications.
Also integral to the 5G setup is that 5G Core Network (5GC) we also mentioned above. The 5GC is fully virtualized and based on cloud-native architecture. This modern foundation allows for innovative features like network slicing (which you met earlier), enabling the operation of multiple virtual networks on the same physical hardware. You can isolate each network and customize it to cater to specific needs and services.
Even better, network slicing can help MVNOs and other CSPs protect one customer segment from events that are affecting another. (To picture this in practice, imagine that a drought-driven wildfire is creating a spike in sensor and communications traffic among agricultural operations in a given region. With network slicing, a CSP can protect their enterprise customers in other industries – say, a large delivery company that uses a lot of vehicle tracking sensors – from delays and outages due to that higher agricultural data traffic. Same goes for their regular retail voice and text traffic. With 5G and network slicing, those customers also would not be affected.)
What will it be like to live on the “edge”?
And remember that edge computing we talked about? Keeping the data closer to the end users (and so keeping that latency super low) is a crucial pillar of 5G speed… and what it will support. Much in the same way that 4G speed enabled the success of streaming services like Prime and Spotify, 5G is likely to enable the expansion of completely new tiers of the entertainment industry. Just as a start, think AR and VR brands becoming as ubiquitous as Neftlix. From there? Who knows where we’ll go.
What other technological innovations are implemented in 5G platforms?
Two further technological innovations you’ll find in 5G platforms are Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV). These provide the agility and flexibility needed to manage complex network configurations and service demands dynamically. 5G systems also use advanced data analytics tools. These help in predicting network loads and potential service issues before they affect users.
Which Brings Us to Function
Let’s discuss the elephant in the room – the biggest 5G question there is. Why develop 5G at all?
Two words: use cases. 5G is a frontier for the experimenters and innovators. (To leverage an analogy, think of all the use cases for electricity that were conceived of after it was invented. It starts with a lightbulb, and eventually you get air fryers, computers, drones, Roombas, EVs, the internet itself…)
With all the experimenting that’s going on, unique and varied benefits of 5G are popping up all over. So let’s look first at the primary function of 5G. From there, we’ll look at a few of the innovative use cases that are growing up around it.

What are the primary functions of 5G in the network infrastructure?
5G’s primary functions in the network infrastructure revolve around significantly enhancing connectivity to support a wide range of applications across different industries. 5G notably enhances mobile broadband speeds and capacity to support data-heavy applications such as high-definition video and augmented reality. And remember: 5G also drastically reduces latency to milliseconds, which is crucial for the many emerging real-time applications that need immediate response. Think: autonomous driving, remote surgeries, and other world-changing innovations.
Additionally, 5G can handle massive communications across extensive networks of IoT devices, allowing for efficient, large-scale connectivity that earlier standards couldn’t support. 5G also introduces more reliable and efficient private networks, giving enterprises enhanced control and mobility for their operations. This aspect of 5G is particularly beneficial for industries that require high security and personalized network configurations.
Finally, thanks to beamforming and MIMO, 5G improves spectrum efficiency. That allows it to support more users at high data rates without needing additional spectrum.
What are the most promising uses of 5G networks?
One of the most promising uses of 5G wireless networks is Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), which supports the rapidly growing demand for mobile data. (Find a little more on this in the next section.) It also fosters Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC – also discussed soon), which is essential for those emerging technologies we mentioned earlier, like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. Additionally, 5G facilitates Massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC). This enables connectivity for a vast array of IoT devices.
But what does it all mean for business and users?
The advent of 5G technology opens a plethora of new possibilities for both businesses and everyday people. These span faster connectivity, revolutionary applications, and the facilitation of new services. Here are seven of the more significant opportunities that are directly related to the use cases we talked about in the previous section.
1. Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
For users, 5G brings about an improvement in mobile broadband experiences with faster download and upload speeds, higher data capacity, and more reliable connections. This enables high-quality video streaming, more responsive gaming, and smoother media-rich web browsing.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) Expansion
5G facilitates massive IoT, where billions of devices can be connected efficiently without straining the network past its abilities. This is crucial for businesses that deploy sensors and other smart devices across various industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and smart cities. It leads to better data collection and automation.
3. Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC)
This feature of 5G is particularly transformative for critical applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and industrial automation. The ultra-reliable, low-latency nature of 5G ensures that services requiring real-time feedback, such as remote surgeries or real-time control of machinery and vehicles, can be performed without delays.
4. Network Slicing
This allows businesses to create customized networks with specific quality of service parameters tailored to unique business needs. Network slicing supports diverse applications – from emergency services requiring high reliability and availability to entertainment services needing high bandwidth and low latency.
5. Virtual and Augmented Reality
With 5G, both VR and AR technologies can operate more efficiently due to the high data speeds and low latency, enhancing user experiences in gaming, virtual meetings, real estate tours, and training simulations. Businesses can use AR to improve operational efficiency or provide better customer service by overlaying helpful information on real-world objects.
6. Remote Work Capability
The reliability and speed of 5G support a robust remote work environment, allowing for high-quality video conferencing, seamless collaboration, and efficient cloud-based operations. That’s all crucial in the current trend toward more flexible work arrangements.
7. Smart Cities, Agriculture and Infrastructure
5G enables smarter, IoT-based management of infrastructure such as traffic lights and energy grids, or even smart irrigation for farms. For cities, this means improved traffic management, enhanced public safety, and more efficient utility services. That all contributes to a reduction in operational costs, improved urban living, and higher food output.
Will 5G change the landscape of digital communications?
5G claims to revolutionize digital communications by providing ultra-fast internet speeds and highly reliable network performance, underpinning the next generation of digital services from cloud gaming and virtual reality to telemedicine and more immersive educational tools. All that sounds pretty landscape-changing to us. (We also know that the landscape has always and will always change. That’s why we design our platforms, like our billing system, to be easily adaptable to 5G. And to whatever else comes next.)
Are there any challenges and issues associated with the deployment and proliferation of 5G?
Yes, deploying 5G does come with several challenges. First, there’s the need for substantial investment to build out the necessary 5G infrastructure, which can be quite costly. Efficiently managing and allocating the spectrum is another major hurdle. That’s especially true in densely populated urban areas where the demand for bandwidth is high. Additionally, with the increase in the number of connected devices, it is increasingly crucial (and increasingly complex) to ensure the security of 5G communications. These factors together make the deployment of 5G both a challenging and essential endeavor.
The Who’s Who of 5G Providers
So we covered the what and the why, and a bit of the how. That, of course, brings us to the next question: Who are the 5G providers? Let’s take a look at the most important players in the game.

Who are the leading providers of 5G infrastructure?
The leading providers of 5G infrastructure include telecommunications giants such as Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, Samsung, and ZTE. These companies are at the forefront of developing and deploying 5G technologies, offering various hardware, software, and services that facilitate the rollout of 5G networks globally.
What do these providers offer?
These providers offer a range of products and services, including:
- 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) equipment: Such as base stations and massive MIMO antennas.
- 5G core networks: Meaning: advanced software and infrastructure to manage network operations efficiently.
- Network services and consulting: To help telecom operators deploy and optimize their 5G networks.
Any tips on how to choose a 5G provider for your business?
The crux here is seamless integration. When selecting a 5G provider for your business, it’s crucial to ensure that their technology aligns with your existing infrastructure. Second to that comes the ability to get any issues that might crop up resolved swiftly, so consider the level of customer support and technical assistance they offer. Additionally, assess each potential provider’s commitment to innovation and their plans for future technologies. It’s one thing to get a provider who can meet your needs now. But don’t forget that you will also be counting on them to meet your needs two, five, even ten or more years down the road. Are they committed to scaling with you and adapting to whatever new technology shows up in the future?
Finally, of course, that brings us to cost. When comparing 5G providers, make sure to evaluate the financial impact of deploying and maintaining their service.
What trends and innovations exist among 5G providers?
Several key developments are shaping the industry. Open RAN (O-RAN) is gaining traction, promoting more flexible and cost-effective network deployments by standardizing and opening interfaces between network components. There’s also the growing integration of AI and machine learning to optimize network operations and traffic management. Furthermore, a strong focus on sustainability is becoming evident, with efforts to develop energy-efficient technologies to minimize the environmental impact of 5G networks.
What challenges and issues do 5G providers face?
Quite a few! To keep it brief, let’s focus on the top 3:
- Geopolitical tensions: As you might have noticed, it’s getting more than a little tense out there. And it’s hard to build a global network in an era of increasing cross-border clashes. And there are non-battle-related global tensions making things complicated, too, such as the Huawei ban in the US and other countries.
- Spectrum allocation: Each country and region has its own complex regulations to adapt to, not to mention competition for limited radio frequencies. That can be a lot to navigate for 5G providers and companies that want to use their services.
- Technical challenges: Networks are getting increasingly complex and expansive (and therefore expensive). Then layer on top of that the constant race to ensure security against extremely sophisticated and evolving criminal enterprises.
The Quick Hit: All the Top 5G Pros and Cons
As scannable as we tried to make this story, that was a lot to sort through, we know. But we hope we’ve provided you with a decent understanding of the key features of 5G technology. Maybe we even sparked some ideas about its applications along the way! To send you off with a good sense of what matters, let’s summarize the pros and cons of the 5G trend. Like almost any new innovation, 5G presents both clear advantages and some concerns regarding its use. Here are the big ones.
Advantages
- Increased speed: 5G networks are significantly faster than 4G, facilitating quicker download and upload times. That makes for better streaming, gaming, and more – in other words, a better user experience.
- Reduced latency: 5G dramatically reduces the data delays to milliseconds, enabling real-time applications and services such as autonomous driving and enhanced virtual reality experiences.
- Greater capacity: 5G can handle many more simultaneous connections per square kilometer than previous technologies. That will help support the proliferation of IoT devices and smart city technologies.
- Enhanced bandwidth: 5G offers broader bandwidth to accommodate the growth in data consumption, particularly in densely populated urban areas.
Disadvantages
- Coverage issues: 5G uses higher frequency bands with shorter range. That could lead to challenges in coverage, particularly in rural and indoor environments.
- Infrastructure costs: The shift to 5G could disrupt existing telecommunications frameworks and business operations, necessitating significant adjustments. We’ll need significant investment to build out new 5G network infrastructure, including new cell towers and technology upgrades.
- Device compatibility: Existing devices are not 5G compatible, necessitating the purchase of new devices. While that sounds like a boon for tech retailers, it could actually be a barrier to widespread adoption.
- Security risks: The increased number of connected devices and complex network architecture could potentially open new avenues for cyber attacks and privacy breaches.
- Public concerns: According to the experts, 5G emissions adhere to international health standards and there is no scientific backing to any of the health myths that are circulating. But there is still some public anxiety over the perceived risks. Warranted or not, that anxiety might need mitigating.
How will 5G change industries?
5G has the potential to significantly transform both business and society across various sectors. In smart cities, 5G could improve how traffic is managed. It could also enhance energy utilization and boost the efficiency of public services through better connectivity and real-time data processing. In healthcare, the technology could enhance telemedicine and remote health monitoring, making reliable, real-time communications a linchpin for patient care advancements. Then there’s the manufacturing sector. It could see a shift towards Industry 4.0, characterized by greater automation and efficiency, driven by connected sensors and machines. In education, 5G may enable more immersive learning experiences through augmented and virtual reality technologies. That could transform teaching methods and make education more accessible.
Are You 5G Ready?
Looking to the future, the prospects for 5G and its sustainable development are highly promising. Ongoing research focuses on enhancing network efficiencies, reducing energy consumption, and ensuring that 5G infrastructure supports sustainable growth. Future developments might include more sophisticated forms of network slicing, the integration of AI capabilities for more effective network management, and technological innovations that could further minimize latency and increase throughput. We’re here to empower you to fully leverage the capabilities of 5G. Feel free to get in touch with our PortaOne experts to explore how this technology can enhance your business. We’d love to chat about the specific opportunities it could hold for you.

